Reinforcement learning is one of the fascinating fields of computer science, and it has proven useful in solving some of the toughest challenges of artificial intelligence and robotics. Some scientists believe that reinforcement learning will play a key role in cracking the enigma of human-level artificial intelligence.
But many hurdles stand between current reinforcement learning systems and a possible path toward more general and robust forms of AI. Many RL systems struggle with long-term planning, training-sample efficiency, transferring knowledge to new tasks, dealing with the inconsistencies of input signals and rewards, and other challenges that occur in real-world applications. There are dozens of reinforcement learning algorithms—and more recently deep RL—each of which addresses some of these challenges while struggling with others.
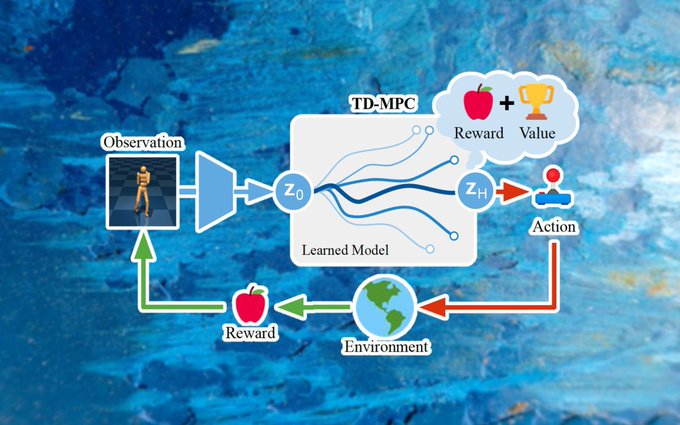
A new reinforcement learning technique developed by researchers at the University of California, San Diego, brings together two major branches of RL to create more efficient and robust agents. Dubbed Temporal Difference Learning for Model Predictive Control (TD-MPC), the new technique combines the strengths of “model-based” and “model-free” RL to match and outperform state-of-the-art algorithms in challenging control tasks.
Mots-clés : cybersécurité, sécurité informatique, protection des données, menaces cybernétiques, veille cyber, analyse de vulnérabilités, sécurité des réseaux, cyberattaques, conformité RGPD, NIS2, DORA, PCIDSS, DEVSECOPS, eSANTE, intelligence artificielle, IA en cybersécurité, apprentissage automatique, deep learning, algorithmes de sécurité, détection des anomalies, systèmes intelligents, automatisation de la sécurité, IA pour la prévention des cyberattaques.