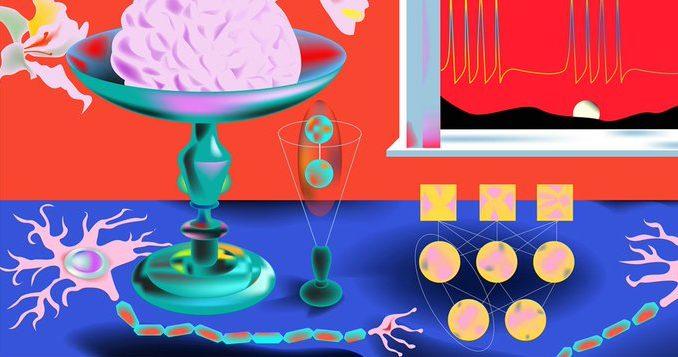
A new model of learning centers on bursts of neural activity that act as teaching signals — approximating backpropagation, the algorithm behind learning in AI.
Every time a human or machine learns how to get better at a task, a trail of evidence is left behind. A sequence of physical changes — to cells in a brain or to numerical values in an algorithm — underlie the improved performance. But how the system figures out exactly what changes to make is no small feat. It’s called the credit assignment problem, in which a brain or artificial intelligence system must pinpoint which pieces in its pipeline are responsible for errors and then make the necessary changes. Put more simply: It’s a blame game to find who’s at fault.
